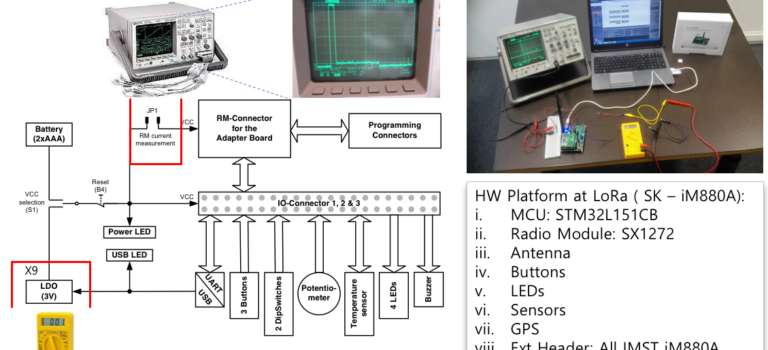
The quest for low-powered and long-range connectivity in the context of Internet of Things (IoT) is ubiquitous. The technology to bridge the low-powered requirements of a connected building scenario and the long range of cellular networks is seen in LoRaWAN. The paper highlights an experiment conducted at Bell Labs. The objective of the experiment is twofold- to verify the published current levels of different operating modes in datasheet and to compare the battery lifetime for the LoRa Class A and C. A high-end current sensing circuit is constructed to gather the voltage levels and temporal variation with increasing payload sizes and spreading factors. Using the Ohmic Law, the battery lifetime and the energy drain could be calculated and compared across the different classes. As predicted the battery lifetime is shorter for Class B than Class A. The energy drain is the greatest for Class C followed by Class B and Class A. It is also observed that the Sleep Mode of Class A displayed a variation of 3 order-of-magnitudes larger than the benchmark values. This could be evidenced due to the underestimated Sleep values used in the publications. This warrants further investigation. Future works can also be directed to the software development, to access the control of the LoRa device using Host Controller Interface via C/C++.
The paper can be found at https://site.ieee.org/benelux-comvt/scvt-2017-conference-program/